
Please improve this section by adding secondary or tertiary sources.įind sources: "cell division" eukaryotic – news This section relies too much on references to primary sources.
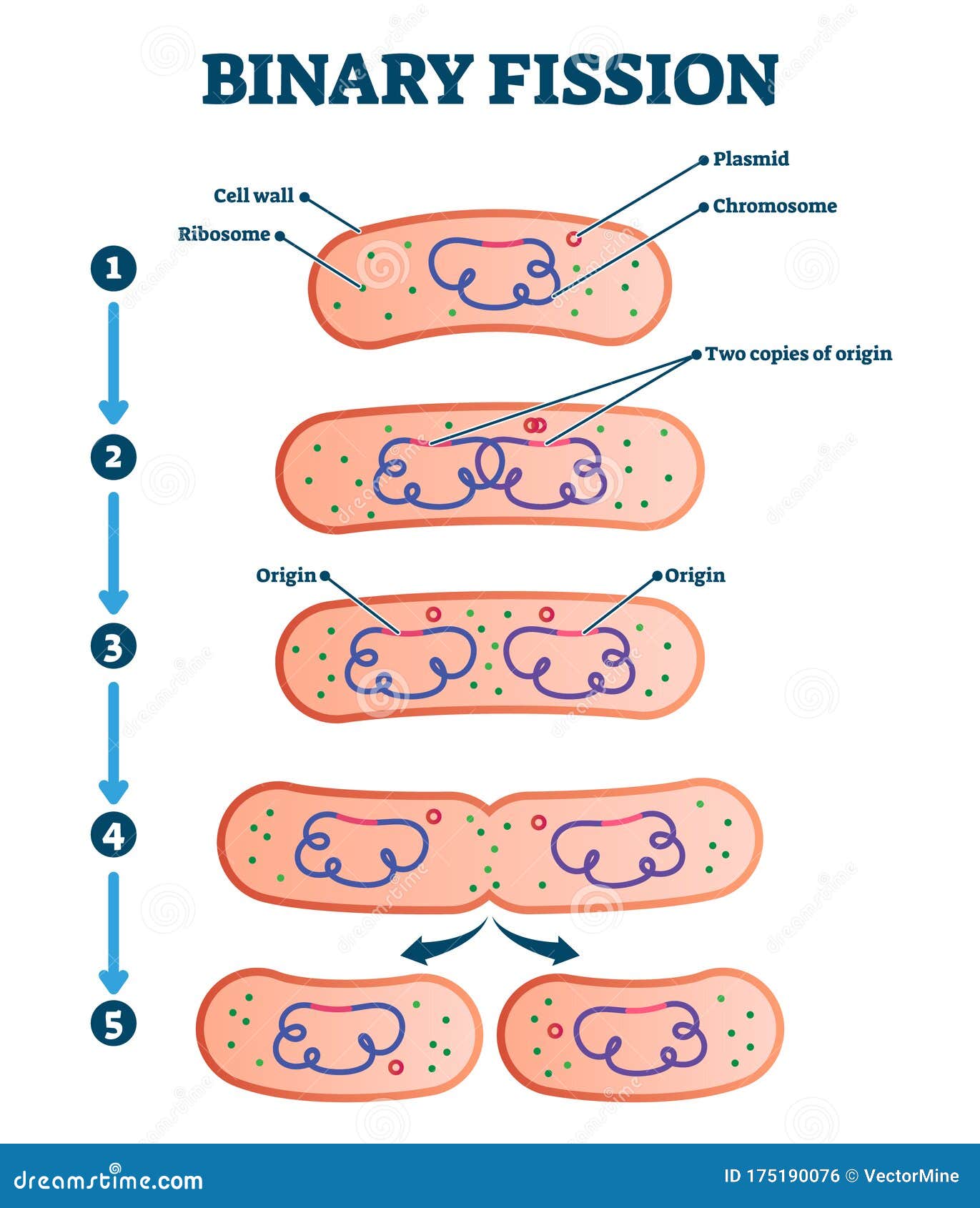
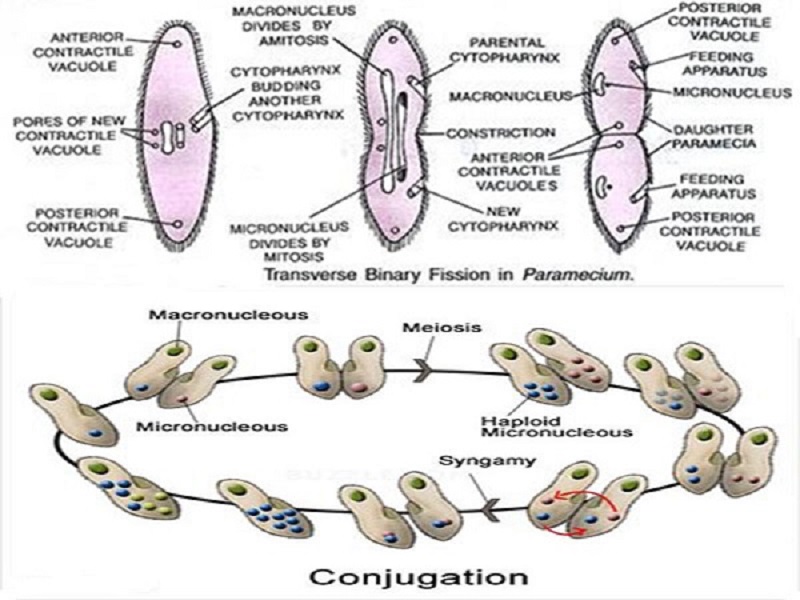
A great deal of cellular infrastructure is involved in ensuring consistency of genomic information among generations. Before division can occur, the genomic information that is stored in chromosomes must be replicated, and the duplicated genome must be cleanly divided between progeny cells. The primary concern of cell division is the maintenance of the original cell's genome. The human body experiences about 10 quadrillion cell divisions in a lifetime. After growth, cell division by mitosis allows for continual construction and repair of the organism. Mitotic cell division enables sexually reproducing organisms to develop from the one-celled zygote, which itself is produced by meiotic cell division from gametes. On a larger scale, mitotic cell division can create progeny from multicellular organisms, such as plants that grow from cuttings. All cell divisions, regardless of organism, are preceded by a single round of DNA replication.įor simple unicellular microorganisms such as the amoeba, one cell division is equivalent to reproduction – an entire new organism is created. While binary fission may be the means of division by most prokaryotes, there are alternative manners of division, such as budding, that have been observed. Prokaryotes ( bacteria and archaea) usually undergo a vegetative cell division known as binary fission, where their genetic material is segregated equally into two daughter cells. Both are believed to be present in the last eukaryotic common ancestor. Both of these cell division cycles are used in the process of sexual reproduction at some point in their life cycle. Homologous chromosomes are separated in the first division, and sister chromatids are separated in the second division. Meiosis results in four haploid daughter cells by undergoing one round of DNA replication followed by two divisions. The different stages of mitosis all together define the mitotic ( M) phase of animal cell cycle-the division of the mother cell into two genetically identical daughter cells. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is preceded by the S stage of interphase (during which the DNA replication occurs) and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis which divides the cytoplasm, organelles, and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components.

Cell division gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. In cell biology, mitosis ( /maɪˈtoʊsɪs/) is a part of the cell cycle, in which, replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. In eukaryotes, there are two distinct types of cell division a vegetative division, whereby each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell ( mitosis), and a reproductive cell division, whereby the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells is reduced by half to produce haploid gametes ( meiosis). Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle. Cell division in prokaryotes ( binary fission) and eukaryotes ( mitosis and meiosis)Ĭell division is the process by which a parent cell divides, when a mother cell divides into two or more daughter cells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
